Modeling Overproduction
Overproduction: This model demonstrates the concept of Overproduction. Overproduction is considered one of the 8 wastes because when the quantity of produced goods exceeds customer demand, it leads to wasted effort and materials, often resulting in the disposal or scrapping of unused products.
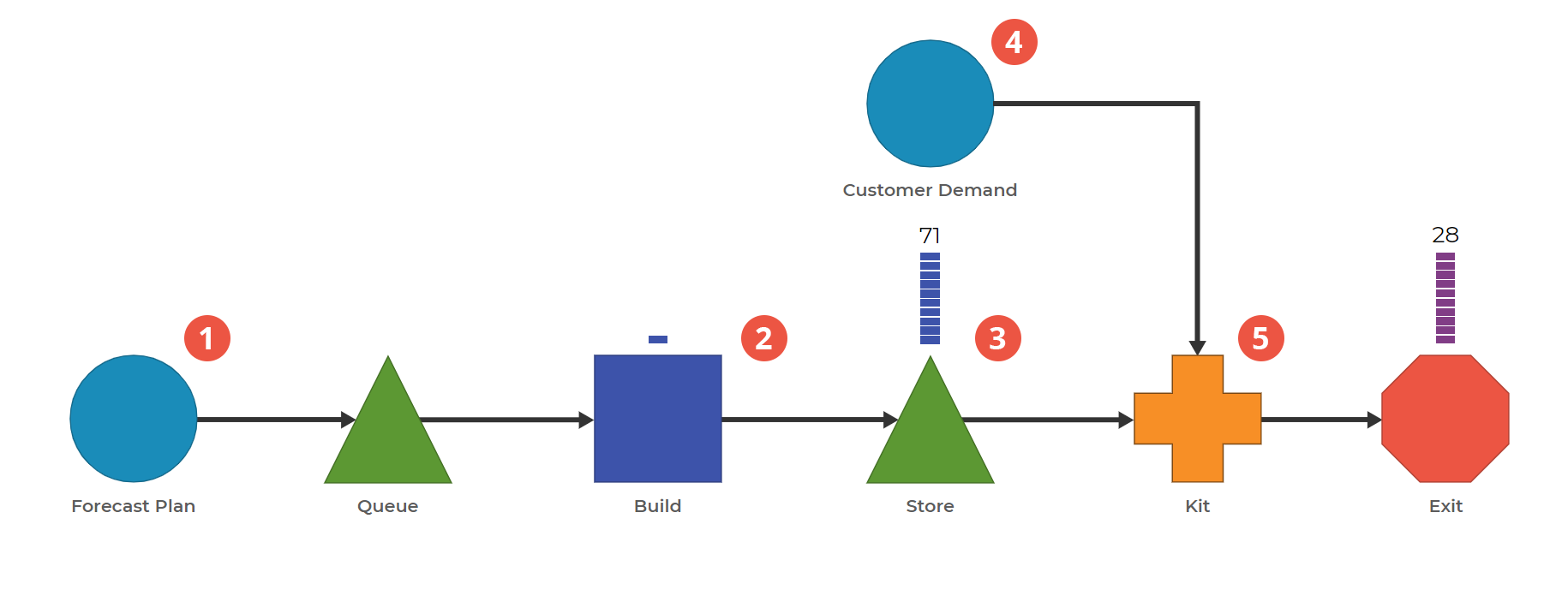
0. There are three items in this model: Forecasted Item, Customer Demand, and Completed Order.
1. Create products based on Forecasted Demand. The Forecast Plan block creates a Forecasted Item on a certain cadence.
2. Demonstrate the time to build the product. This Activity Block represents the time to build the item. It runs continuously throughout the model, creating products based on the forecasted demand.
3. Store products. This Queue Block holds finished goods that are waiting for customer demand.
4. Model Customer Demand. Customer demand does not line up directly with the forecasted plan. In fact, demand stops after some time, possibly representing an upgraded product or a competitor product coming on the market.
5. Combine Forecasted Item with Customer Demand to complete an order. This step represents the consumption of the product over time.
Notice how there is an excess of product in the Store. When demand for the product stops, what happens to the inventory that has been created? How can you account for the time spent building those products, the raw materials used, and the storage and transportation costs associated with keeping those products available?
While some may say there is a practical need for additional inventory, the ideal situation involves matching production exactly with demand.
Was this helpful?
