Writing a Book
Writing a Book. This process highlights looping back to other parts of the process.
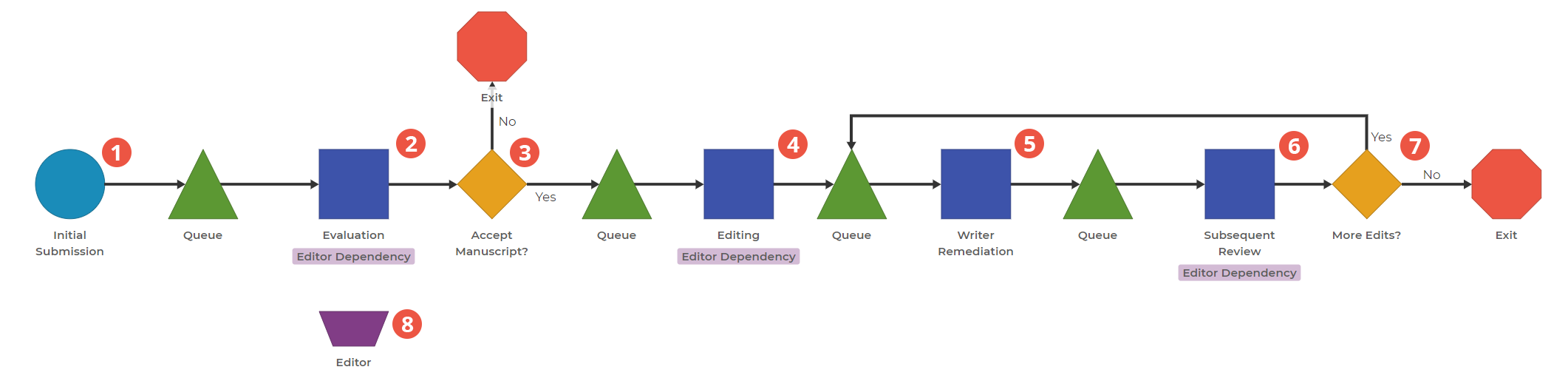
0. There is one item: Manuscript.
1. Writers submit manuscripts to the Editor. Manuscripts that come in must wait until the Editor is available.
2. The Editor evaluates the manuscripts. There is a lot of variation in the time this can take. By setting the Processing Time to a triangular distribution with a minimum, mode, and maximum, we can model this variation as applied to different manuscripts.
3. Decide whether to Reject or Accept the manuscript. This Decision Block routes rejected manuscripts out of the process and passes accepted ones forward.
4. Once a Manuscript is accepted, the editing process begins. In this case, we've separated the first draft editing since the first time might be unique compared to subsequent evaluations.
5. Writer Remediation. This Activity Block has 9999 Servers Available. Why? Because each manuscript has an individual writer, and the writers can work on their own manuscripts at the same time. Therefore, we want to have the maximum available to allow all manuscripts to move on in the process, simulating being sent to the respective writer.
6. Subsequent Review. When the writer sends the manuscript back, the Editor will review it again.
7. The Editor then decides whether to add additional comments for the writer or finalize it and continue with the process. This Decision block routes the manuscript the correct way.
8. This Resource Block represents the Editor, who must complete multiple steps in this process on various manuscripts. This ensures the time is split among the steps, and one Editor completes them all.
Book editing might be a unique case for discrete event simulation, but it highlights the use of some common blocks. The Activity Block represents all of the work that goes into the process. The Decision Block splits the path for items to allow different steps to happen to different items. In this case, the Resource Block separates out the people doing the work from the Activities themselves, allowing resources to be split across multiple activities.
Was this helpful?
