Kruskal Wallis Test Tutorial
When to use this tool
The Kruskal Wallis Test is used to compare the medians of three or more independent, continuous populations. As an example, three treatments are administered to randomly sampled groups of patients and their median scores on a reaction time test compared.
The Kruskal Wallis test makes the following assumptions:
- The data are continuous numeric.
- The units are randomly sampled.
- The groups are independent of each other.
- The groups have equal variances.
Using EngineRoom
Note: You must have raw data to run this test. Non-parametric tests cannot be run with sample summary data.
Example:
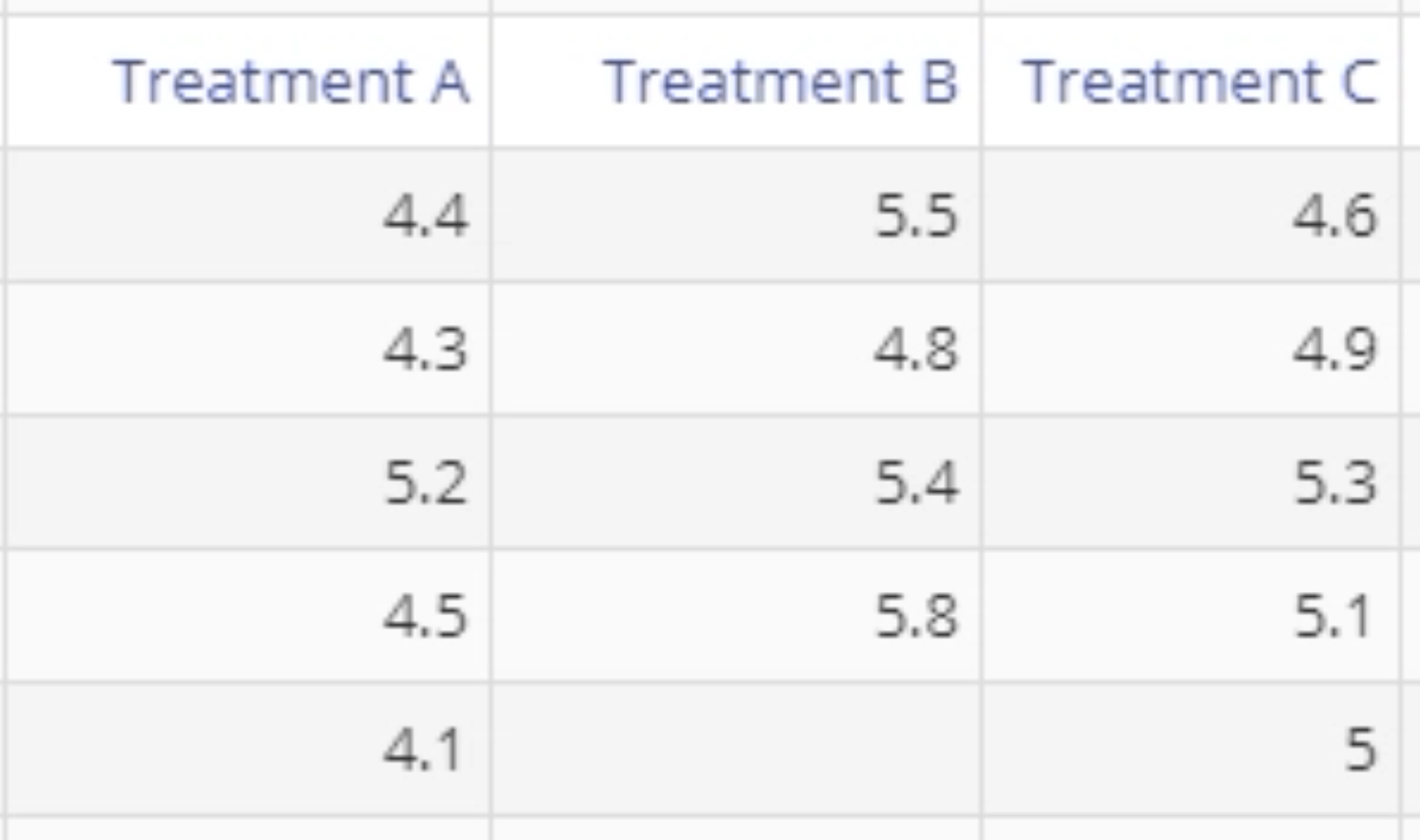
The data for this example consists of three samples of scores representing reduction in pain, for each treatment group: A, B and C. We want to test, at the 15% level, whether the reduction in pain differs across treatments.
Steps:
- Select the Analyze menu > Non-parametric > Click on the Kruskal Wallis Test.
- Click on the data file in the data sources panel and drag the three Treatment variables onto the Data variable drop zones on the study.
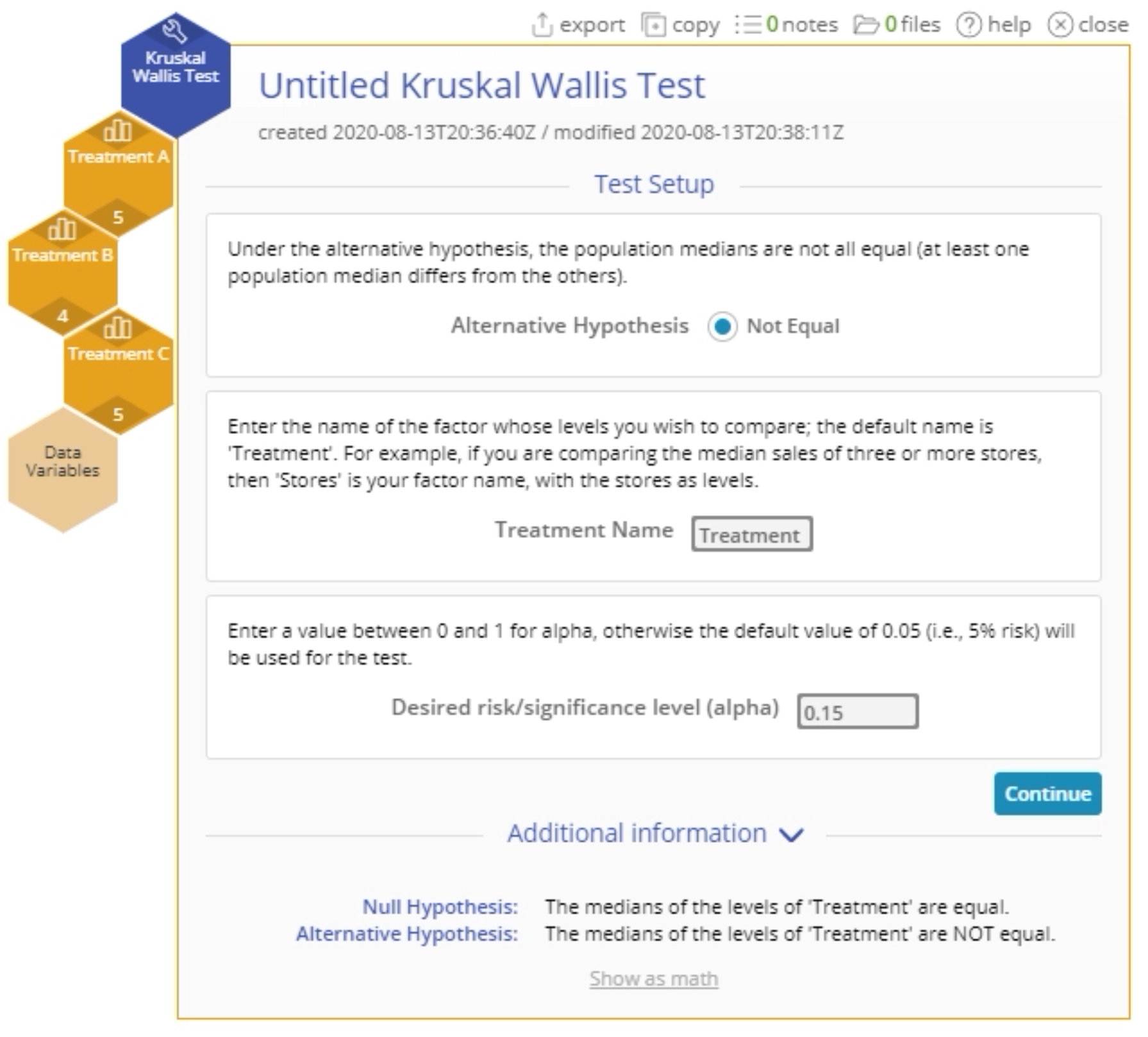
- Set up the test as shown, and click Continue:
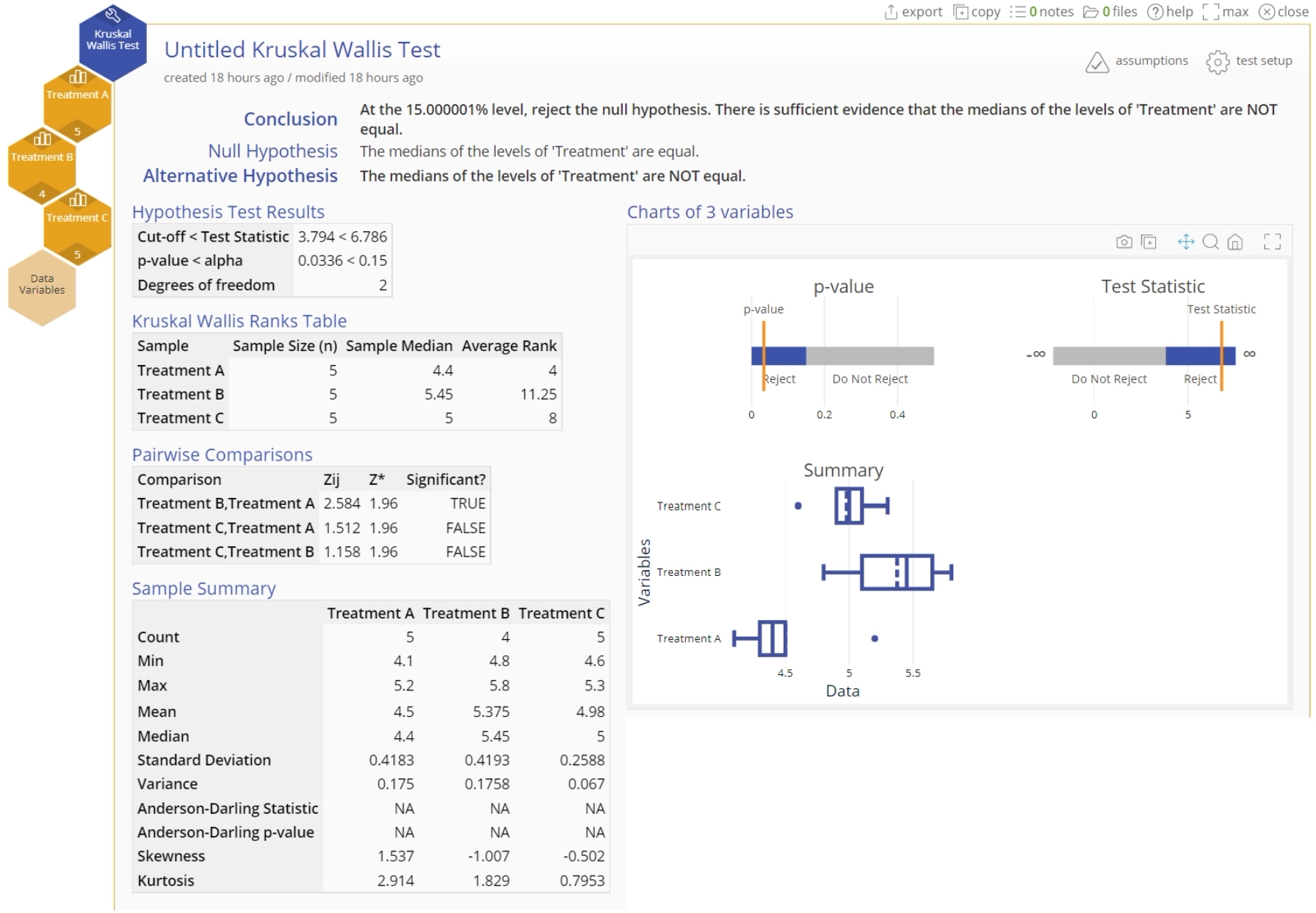
- The Kruskal Wallis Test output is shown:
The p-value is less than the chosen significance level of 15%, so reject the null hypothesis; at least one treatment differs significantly from the others at the 15% level. The Pairwise Comparisons table shows that in particular, Treatments A and B differ significantly.
Kruskal Wallis Test Video Tutorial
Instructor Resources
Was this helpful?